Bayesian statistical fitting is a powerful technique for data analysis that allows us to incorporate prior information and update it with observed evidence. In this blog, we’ll explain how to perform a Bayesian fit for linear regression using Python, with the goal of estimating the model parameters while quantifying uncertainty.
This tutorial describes step by step how to perform a Bayesian Statistical fit for Linear Regression
pip install pymc3 numpy matplotlib seaborn
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns import pymc3 as pm
# Generate data
np.random.seed(42)
n_samples = 200
X = np.linspace(0, 10, n_samples)
true_intercept = 1.0
true_slope = 2.5
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, n_samples)
# Observed data
Y = true_intercept + true_slope * X + noise
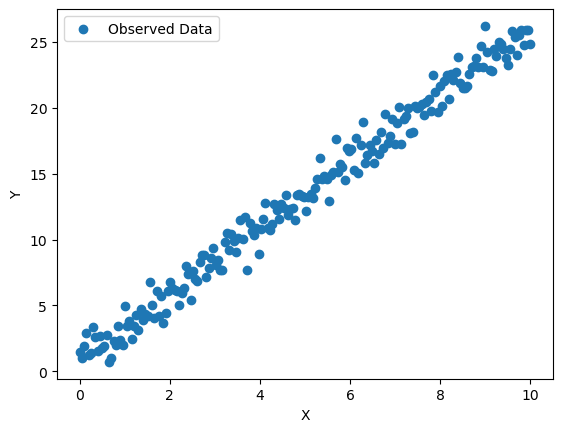
# Plot the data
plt.scatter(X, Y, label='Observed Data')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Define the Bayesian model
with pm.Model() as bayesian_model:
# Priors for the parameters
intercept = pm.Normal('intercept', mu=0, sigma=10)
slope = pm.Normal('slope', mu=0, sigma=10)
sigma = pm.HalfNormal('sigma', sigma=1)
# Linear regression model
mu = intercept + slope * X
# Likelihood
Y_obs = pm.Normal('Y_obs', mu=mu, sigma=sigma, observed=Y)
# Inference
trace = pm.sample(1000, tune=1000, cores=2, target_accept=0.95)
In this model:
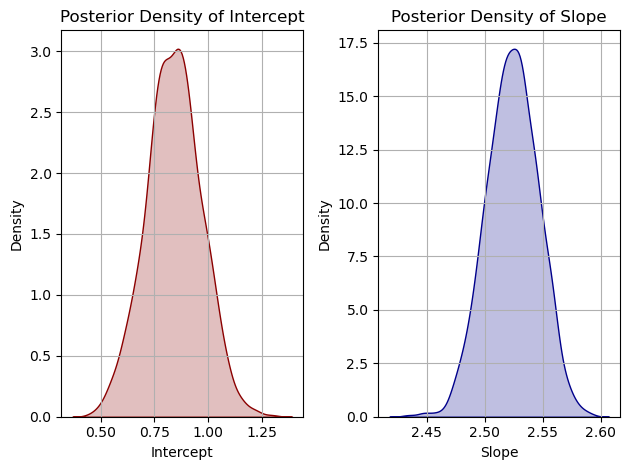
Priors are initial assumptions about the parameters, specified as normal distributions in this case.
Likelihood models the relationship between the observed data and the model parameters.
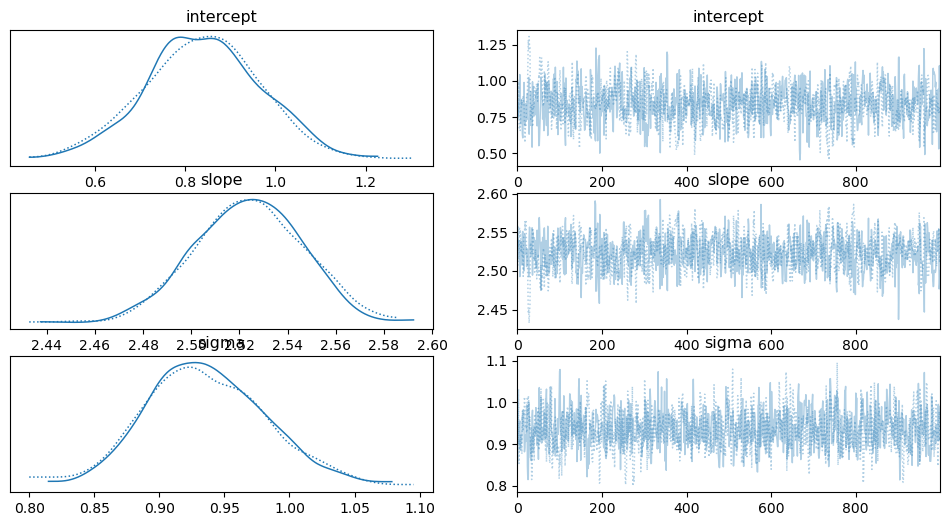
# Summary of the results pm.summary(trace) # Plot the posterior distributions pm.traceplot(trace) plt.show()
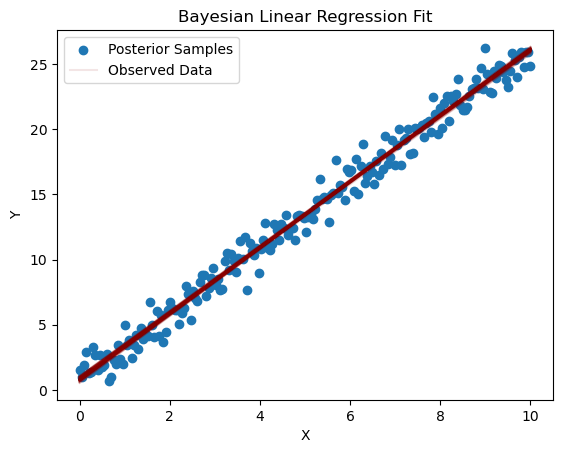
# Generate posterior predictive samples
with bayesian_model:
posterior_pred = pm.sample_posterior_predictive(trace, var_names=['intercept', 'slope'], samples=100)
# Plot the predictions
plt.scatter(X, Y, label='Observed Data')
for i in range(100):
pred_y = posterior_pred['intercept'][i] + posterior_pred['slope'][i] * X
plt.plot(X, pred_y, color='darkred', alpha=0.1)
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.title('Bayesian Linear Regression Fit')
plt.legend(['Posterior Samples', 'Observed Data'])
plt.show()
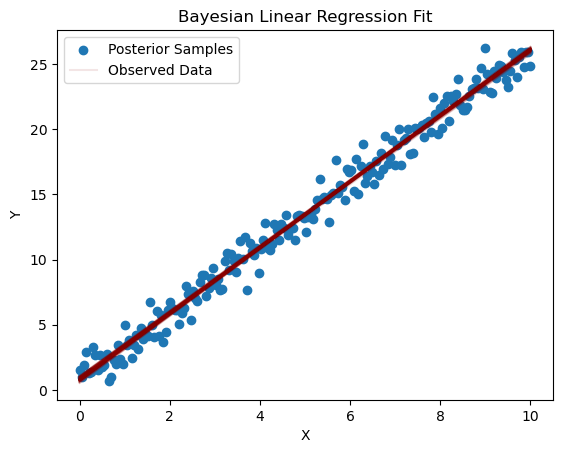


Ejemplo inicial de ajuste bayesiano que contiene todos los elementos interesantes de la metodología
Muy interesante!! Gracias.